
“The beautiful game is like a dance of life.” – Pelé
Welcome to your comprehensive guide to soccer, where we explore the intricacies of this universally loved sport. Known widely as “the beautiful game,” soccer transcends borders, languages, and cultures, uniting fans and players around the globe. From the amateur fields to grandeur stadiums filled with passionate spectators, soccer’s global appeal is undeniable. This guide dives into the sport’s rich history, essential rules, tactical strategies, and the vibrant culture that surrounds it.
Published on July 18, 2023, “Soccer: The Beautiful Game’s Ultimate Guide” offers an exclusive look into recent tournaments, including results from the Qatar 2022 Men’s World Cup and insights into the upcoming 2023 Women’s World Cup in Australia and New Zealand. This 408-page book encompasses everything you need to know about soccer, featuring stats and facts on players, clubs, and historical matches, along with captivating illustrations that depict the fascinating elements of the sport.
In this guide, we unravel player roles, essential strategies, and cultural traditions, ensuring that both new fans and seasoned aficionados discover the depth of this remarkable game. From the joyful sounds echoing through packed stadiums to the quiet determination of youth players striving to make their mark, soccer remains a captivating pursuit that inspires a sense of belonging and collective passion.
Key Takeaways
- Soccer is celebrated as the most popular sport worldwide.
- The guide includes crucial information on recent World Cup tournaments.
- Features include player statistics, iconic matches, and football culture.
- This comprehensive resource caters to both fans and aspiring players.
- The guide simplifies complex concepts with clear, jargon-free explanations.
Introduction to Soccer and Its Global Appeal
Soccer, known as football in many parts of the world, boasts an impressive global appeal that draws fans and players from diverse cultures and backgrounds. With more than 240 million registered soccer players globally, the sport transcends borders and fosters a sense of community among enthusiasts. FIFA, the governing body for soccer, includes 205 member associations across six confederations, illustrating the widespread soccer interest found in various continents.
The international football popularity is further exemplified by the massive viewership of events such as the FIFA World Cup, which captivated around 3.5 billion viewers during the 2018 tournament, positioning it as the most-watched sporting event in history. This staggering number highlights how soccer acts as a cultural touchpoint that unites individuals from different nations.
Leagues like the English Premier League and Spain’s La Liga have transformed soccer into a multi-billion-dollar industry, attracting global sponsors and broadcasters. In the United States, Major League Soccer (MLS), founded in 1993, comprises 27 teams and continues to grow in popularity. The integration of high-profile players into leagues further fuels this soccer interest, as fans eagerly support their clubs and stars.

- FIFA generates most of its revenue through television broadcast rights and advertisements for events like the World Cup.
- The economic impact of hosting major soccer events enhances local job markets and infrastructure.
- Despite disparities in wealth between clubs, player salaries dominate club revenues, particularly in Europe.
As soccer continues to evolve and establish its roots across various nations, it remains a powerful catalyst for international relations and cross-cultural exchange. The popularity of this remarkable sport engages billions, making it a dynamic force in our ever-connected world.
The History of Soccer: From Folk Rituals to Global Spectacle
The history of soccer is a fascinating journey that spans across centuries and continents. It has evolved from informal folk rituals into a structured and celebrated global sport. The earliest documented kicking game, known as _cuju_, originated in ancient China during the fourth century B.C., while the indigenous Australians had their own kicking game, _marn gook_, with roots that extend back thousands of years. Mesoamerican civilizations also engaged in ball games which utilized rubber balls propelled with the hips, showcasing the diverse forms of football-like activities that have existed throughout history.
Modern soccer began to take shape in the British Isles, where various folk football games emerged during medieval times. With different regions adopting their unique rules and customs, the need for standardization became apparent. The 19th century marked significant progress in the evolution of football in Britain, especially with efforts to codify the sport, leading to the establishment of formalized leagues.
The term “soccer” itself originated in England in the 1880s, serving to distinguish association football from rugby football. The establishment of FIFA in 1904 represented a crucial milestone in soccer heritage, uniting various national associations under one governing body. This paved the way for soccer to be included in the Olympic Games in 1908 and culminated in the first FIFA World Cup held in 1930. Since then, the World Cup has remained a prominent event every four years, contributing significantly to the global profile of the game.
Today, the history of soccer continues to inspire approximately five billion followers worldwide. In the United States, soccer has rapidly grown, with over 13 million individuals participating, making it the third most played team sport in the country. Events like the World Cup Final have drawn massive audiences; for instance, about 24 million American viewers tuned in for the 2010 final. The youth soccer scene in the U.S. boasts the highest participation rate globally, with around 4 million registered players, underscoring the sport’s deepening roots in American culture.

Understanding the Soccer Field: The Pitch and Its Markings
The soccer field, also referred to as the pitch, plays a central role in the game. Its dimensions and specific markings in soccer not only define the playing area but also significantly impact game strategy and flow.
Typically, a soccer field ranges from 100 to 130 yards in length and 50 to 100 yards in width. In international play, the standards tighten, with fields measuring between 110 to 120 yards long and 70 to 80 yards wide. The goal is a critical element of the field, measuring 8 yards wide and 8 feet high, designed with nets to clarify when a goal is scored.
Key areas of the field include:
- Goal Area: Extends 6 yards from the goal posts.
- Penalty Area: Reaches 18 yards from the goal posts, often called the 18-yard box.
- Penalty Mark: Located 12 yards away from the goal line, positioned centrally for penalty kicks.
- Center Circle: A crucial feature with a diameter of 10 yards, used during kick-offs.
- Corner Arc: This area, 1 yard in diameter, marks the corner kick spot.
Flag posts at each corner are required to stand at least 5 feet tall for player safety. Both the center line and goal lines correspond with pitch dimensions, varying from 50 to 100 yards across standard games. In international matches, the touchlines typically measure between 110 to 120 yards long.
Another significant marking is the Penalty Arc, a half-circle with a 10-yard radius around the penalty area, ensuring that players maintain the required distance during penalty kicks.

Understanding these elements of the soccer field enables players and coaches to strategize effectively, ensuring a competitive edge based on the specific measurements and markings in soccer. Each match presents unique challenges influenced by pitch dimensions, making the layout foundational to the beautiful game.
Key Rules of Soccer: What Every Fan Should Know
Understanding the essential soccer rules enhances the viewing experience. Knowledge of the offside rule, free kicks, and corner kicks plays a pivotal role in grasping the game’s dynamics. This section delves into these vital components, providing clarity and insight into their application during matches.
The Offside Rule Explained
The offside rule is crucial to maintaining the flow of soccer. This rule states that an attacking player is considered offside if they are closer to the opponent’s goal line than the second-last defender when the ball is played to them. An important aspect is that only attackers can be offside, which means defenders can position themselves strategically while defending their goal. Understanding this rule can significantly impact game strategy and player positioning, ensuring a balanced contest on the pitch.
Understanding Free Kicks and Corner Kicks
Free kicks and corner kicks create vital opportunities for scoring in soccer. Free kicks result from fouls and can be classified into direct and indirect types. A direct free kick allows the player to shoot directly at the goal, while an indirect kick requires another player to touch the ball before a goal can be scored. These kicks can shift the momentum of the game and provide a critical scoring chance.
Corner kicks occur when the ball goes out of bounds beyond the end line, last touched by a defender. This grants the attacking team an opportunity to deliver the ball into the penalty area, often leading to scoring possibilities. Familiarity with these set pieces enhances a fan’s appreciation for the game and showcases the skill involved in executing them effectively.

Positions in Soccer: The Roles of Players on the Field
Understanding the various soccer positions and their specific player roles is essential to grasping the game’s dynamics. Each soccer team consists of 11 players, including a goalkeeper and 10 outfield players. Different formations, like the popular 4-2-3-1, highlight the critical roles of strikers and defenders, each contributing in unique ways during play.
The Role of the Goalkeeper
The goalkeeper occupies the #1 spot and has unique responsibilities that set them apart from other players. Their primary function is to prevent goals, requiring a combination of skills like catching, shot-stopping, and organized communication with the defense. Goalkeepers operate mainly within their penalty area, where their specialized skills in footwork and reflexes become vital. Proper positioning is crucial for goalkeepers to react swiftly to opposing strikers’ shots, making their role indispensable to the team’s overall success.
Key Responsibilities of Strikers and Defenders
Strikers and defenders each play pivotal roles that define their soccer positions on the field. Strikers, often positioned as forwards, focus on advancing toward the opponent’s goal to create scoring opportunities. Within this category, center forwards typically occupy the #9 spot, aiming to score through agility and striking capabilities. Second strikers operate between forwards and midfielders, enhancing offensive plays by assisting in goal creation.
Defenders, on the other hand, aim to thwart attacking plays initiated by strikers. They begin their positions close to the goal line and operate across various roles such as center-backs, who focus on stopping opposing attacks, and full-backs, who defend against wingers while supporting the center-backs. The intricate blend of defensive responsibilities ensures that teams maintain stability while preventing forwards from easily accessing scoring chances.
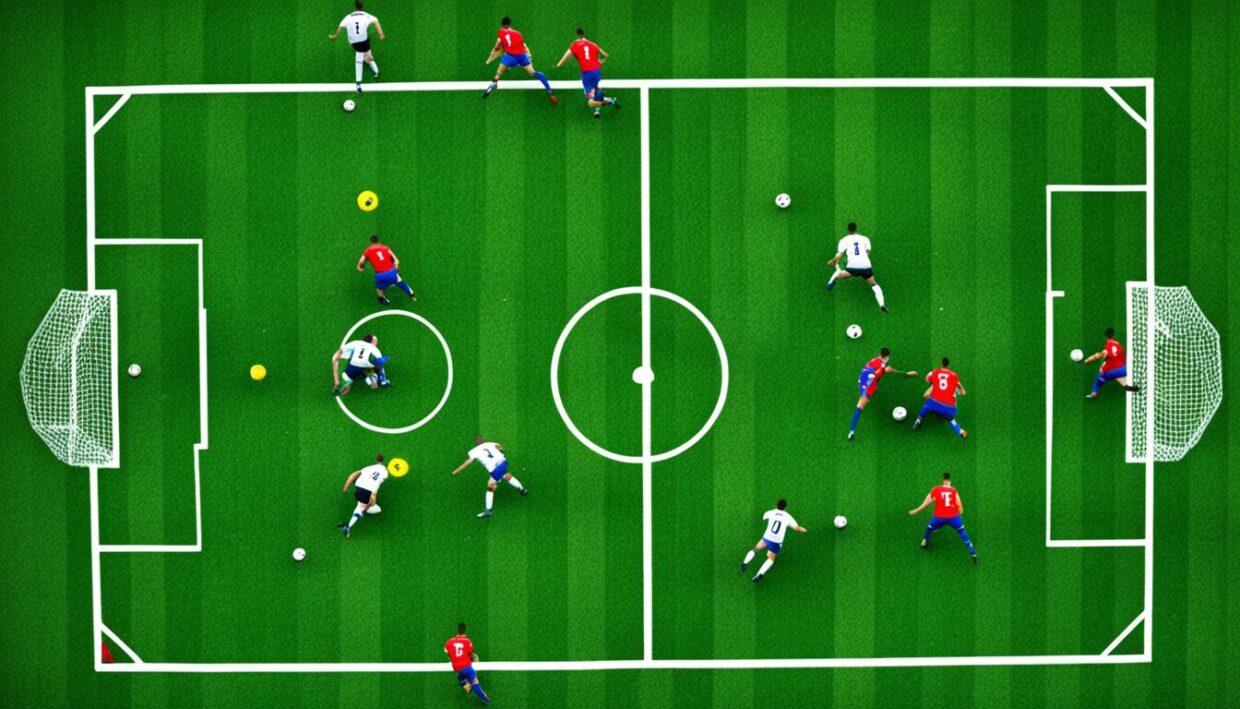
Soccer Tactics: Formations and Strategies
Understanding soccer tactics is crucial for analyzing how teams gain advantages during matches. Different formations shape gameplay strategies, affecting player roles, responsibilities, and overall performance on the pitch. Here are some notable formations and their tactical implications:
| Formation | Player Structure | Key Strengths | Potential Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-3-3 | 4 Defenders, 3 Midfielders, 3 Forwards |
|
Might struggle against formations with more midfielders. |
| 4-4-2 | 4 Defenders, 4 Midfielders, 2 Forwards |
|
Less control against 4-3-3 or 4-2-3-1 formations. |
| 3-5-2 | 3 Defenders, 5 Midfielders, 2 Forwards |
|
Potential vulnerability on the flanks. |
| 4-2-3-1 | 4 Defenders, 2 Defensive Midfielders, 3 Attacking Midfielders, 1 Forward |
|
Can be susceptible to counter-attacks if midfielders don’t track back. |
Adaptability in soccer tactics showcases the dynamic nature of formations. A team’s choice may change based on various factors, such as opposition strategy and match context. For instance, a losing team might shift to a more attacking formation like 4-3-3 to enhance their offensive capabilities. Teams like Liverpool and Barcelona utilize 4-3-3 to capitalize on aggressive play, while others like Atlético Madrid thrive under the balanced 4-4-2. Each tactical setup brings its unique advantages and challenges that can ultimately dictate the outcome of the match.

The Importance of Soccer Leagues: A Look at Major Competitions
Soccer leagues play a crucial role in the development and popularity of the sport worldwide. They serve as platforms for talent discovery, competition, and fan engagement, impacting both local and international soccer competitions. Among these leagues, the Premier League stands out as a benchmark for quality, attracting millions of viewers and showcasing some of the best talents in the game.
Overview of the Premier League
The English Premier League, formed in 1992, has become the most-watched soccer league globally. It generates the highest revenue among all soccer leagues and includes 20 of the top clubs in England. Manchester United, with 13 titles, is the most successful club in the league’s history. This league is renowned for its competitiveness, where even lower-tier teams can challenge the giants, showcasing the unpredictable nature of the sport.
Comparing Major Soccer Leagues Worldwide
There are numerous soccer leagues worldwide, each bringing its unique flavor to the game. While the Premier League leads in viewership, competitions such as La Liga in Spain, Serie A in Italy, and Bundesliga in Germany also hold significant influence. For instance, La Liga, established in 1929, features elite clubs like Real Madrid and Barcelona, boasting rich histories and rivalries that enhance their appeal. The table below summarizes key aspects of these major leagues:
| League | Founded | Top Clubs | Titles Record |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premier League | 1992 | Manchester United, Liverpool, Chelsea | 13 (Manchester United) |
| La Liga | 1929 | Real Madrid, Barcelona, Atletico Madrid | 34 (Real Madrid) |
| Serie A | 1898 | Juventus, AC Milan, Inter Milan | 36 (Juventus) |
| Bundesliga | 1963 | Bayern Munich, Borussia Dortmund | 31 (Bayern Munich) |
| Ligue 1 | 1933 | Paris Saint-Germain, Marseille | 10 (Saint-Étienne) |

This comparison illustrates the variations in success and historical significance among different soccer leagues, further emphasizing the immense popularity and global nature of soccer. As clubs participate in international competitions, they continuously raise the bar, making the sport more enthralling for fans around the world.
Highlighting Legendary Soccer Players and Their Impact
The world of soccer is filled with legendary soccer players who have shaped the sport in remarkable ways. Their contributions extend beyond their technical skills; they influence culture and inspire generations. Among them, famous strikers and iconic goalkeepers have marked history with their incredible feats on the pitch.
Famous Strikers Who Changed the Game
Famous strikers such as Pelé and Diego Maradona are often celebrated for their exceptional talent and ability to change the course of matches. Pelé’s record of 643 goals in 659 games highlights his prowess and enduring legacy. Maradona, best known for leading Argentina to victory in the 1986 World Cup, showcased skills that mesmerized fans and boosted soccer’s popularity globally. Today, Cristiano Ronaldo and Lionel Messi continue to dominate the scene, with Ronaldo achieving an astonishing 123 goals for Portugal in international competitions and Messi netting 672 goals in 778 appearances for Barcelona.
Iconic Goalkeepers and Their Legends
Transitioning to the defensive side, iconic goalkeepers like Gianluigi Buffon and Lev Yashin have left indelible marks on the game. Buffon’s leadership and shot-stopping abilities have not only solidified his status as one of the best goalkeepers but also inspired countless young players aspiring to follow in his footsteps. Yashin, regarded as the only goalkeeper to have won the Ballon d’Or, transcended the traditional role and redefined what it meant to be a goalkeeper in soccer. Their styles and approaches to the game remind fans that greatness comes in various forms on the soccer field.

Understanding Soccer Culture: Fans and Traditions
The world of soccer culture thrives on vibrant fan traditions and the deep-rooted connections within the soccer community. Different fans contribute to the atmosphere through diverse expressions of passion, making each match a unique experience. Traditional chants, banners, and colorful displays create an electrifying environment, enhancing the connection between supporters and their teams.
Rivalry games amplify this excitement, with fans bringing intense competition to the stands. The experience of running through a victory tunnel formed by enthusiastic supporters offers recreational players a taste of the electric atmosphere at major matches. Such moments illustrate how soccer serves as a social glue, fostering unity and local pride among diverse groups.
Items like soccer scarves symbolize loyalty and love for a team, with fans wearing them proudly. The exchange of jerseys at the end of a match between players signifies mutual respect, reflecting the shared ethos within the soccer community. Reports indicate that 43 percent of the global population is interested in soccer, establishing it as the world’s most popular sport.
Despite the joyful experiences, soccer culture also faces challenges. The sport has seen incidents of hooliganism and discrimination, prompting initiatives like the MLS’s “Don’t Cross the Line” campaign to combat racist behavior during matches. The UEFA has similarly sought to address discrimination through its “No to Racism” campaign. Fostering a positive and inclusive environment within the soccer community remains essential for the continued growth and appreciation of the sport.

Soccer’s Role in Major Tournaments: FIFA World Cup Highlights
The FIFA World Cup is the pinnacle of international soccer, showcasing the sport’s greatest talents and generating unparalleled excitement among fans worldwide. This tournament not only highlights memorable matches and legendary players but also plays a crucial role in shaping soccer’s tournament history. Watching nations compete on such a grand scale captures the hearts of millions and promotes cultural exchange among diverse audiences.
Memorable moments from various FIFA World Cups stand out, such as surprising victories and intense rivalries that often lead to dramatic conclusions. For example, the quarterfinal match between Portugal and North Korea in 1966 exemplified this thrill, with 40,248 spectators witnessing an intense game that featured Portugal launching an impressive attack.
The tournament has witnessed significant developments over the years. Since its inception, the FIFA World Cup has expanded, leading to a surge in membership for FIFA. From 1939 through 1982, FIFA transformed into a global commercial powerhouse. Modern events like the FIFA Club World Cup and Women’s World Cup have emerged, reflecting the growth of major soccer tournaments in recent decades.
Host countries enjoy economic benefits and enhanced tourism during the FIFA World Cup. Investments in infrastructure, accompanied by increased global engagement through technology, create lasting impacts. FIFA’s initiatives aim to ensure soccer remains accessible, with programs such as the FIFA Forward Development Programme promoting grassroots development.
The integration of technology has modernized soccer, with innovations such as player tracking and analytics enhancing gameplay. Engaging fans through virtual experiences and esports events has further solidified soccer’s significance in today’s digital landscape.
- Expansion of FIFA membership and commercial growth (1939-1982)
- Introduction of FIFA Club World Cup and Women’s World Cup
- Positive economic impact on host countries
- Technological advancements in player performance and fan engagement
- Promotion of grassroots initiatives for soccer accessibility

As we look forward to the upcoming FIFA World Cup events in the United States in 2026, the anticipation continues to grow. The collaboration between various organizations and strategic partners aims to enhance accessibility, ensuring that soccer remains a vital component of local communities and a pivotal player in the landscape of major soccer tournaments.
| FIFA World Cup Highlights | Details |
|---|---|
| First FIFA Ballon d’Or Introduced | 1956, recognizing individual excellence in soccer. |
| Significant Membership Growth | FIFA became a global commercial powerhouse (1939-1982). |
| Introduction of Women’s World Cup | 1983-Present, reflecting the growth in women’s soccer. |
| Economic Impact on Host Countries | Boosted tourism and infrastructure development. |
| Technology and Soccer | Integration of analytics and virtual experiences for fans. |
| Grassroots Development Programs | FIFA Forward Development Programme focused on accessibility. |
Participating in Soccer: From Local Clubs to Professional Teams
Engaging in soccer can be a rewarding experience for aspiring players, providing access to numerous opportunities for skill development and competition. Youth soccer clubs serve as the foundation for many players starting this exciting journey. Choosing the right club significantly influences a player’s sports experience and growth in the game.
How to Choose a Soccer Club for Youth Players
When selecting a youth soccer club, parents and players should consider several factors to ensure a fruitful experience:
- Coaching Quality: It’s essential to evaluate the coaching staff’s credentials and their approach to teaching the game. A well-structured development program can enhance players’ skills.
- Club Values: Understanding the club’s philosophy and values can help align expectations and supportive environments for youth athletes.
- Facilities: Access to good training resources and fields can significantly affect skill acquisition and enjoyment of the game.
- Competitive Level: Determining whether the club competes in recreational leagues or advanced tournaments informs players’ scope of development.
Participation in youth soccer clubs lays a solid foundation for players, guiding them towards the ultimate goal of achieving a path to professional soccer.
The Path to Becoming a Professional Soccer Player
Transitioning from local youth soccer clubs to the professional level involves dedication and strategic planning. Aspiring players often need to:
- Join Competitive Leagues: Many journey to professional status begins with participation in competitive leagues that showcase talent.
- Participate in Academies: Soccer academies offer specialized training and connections to scouts looking for professional prospects.
- Commit to Continuous Learning: Regularly practicing and attending skill development sessions is crucial for success in the sport.
Involvement in youth soccer provides valuable life skills and a deep passion for the game. The commitment to the sport, combined with the right support, plays a pivotal role in setting players on their path to professional soccer.

Soccer Equipment: What You Need to Get Started
When embarking on the journey of playing soccer, having the right soccer equipment is crucial for performance and protection. Players at all skill levels benefit from essential player gear that not only helps enhance their game but also ensures safety on the field. This section explores the fundamental gear needed and discusses the fascinating soccer ball evolution over the years.
Essential Gear for Players
A comprehensive kit starts with properly fitted accessories. Here’s a look at vital equipment:
- Soccer Cleats: Available in sizes from youth to adult, these shoes typically feature molded studs, often ranging from 10 to 14. Molded cleats are advisable for beginners.
- Shin Guards: Key for protection, they come in slip-in styles or strapped-on designs. The appropriate size should leave 2-3 finger lengths between the top of the guard and the knee cap.
- Soccer Socks: Designed to fit over shin guards, these socks are essential for safety and comfort.
- Water Bottles: Staying hydrated is vital during training and games; players should always carry their own.
- Soccer Gear Bags: Backpacks or totes are perfect for carrying all your equipment conveniently to practices and matches.
The Evolution of Soccer Balls
The soccer ball evolution reflects ongoing technological advancements in the sport. Various sizes cater to different age groups, with size 3 for players aged 8 and under, escalating to size 5 for those 13 and older. Key distinctions in soccer balls include:
| Size | Recommended Age | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| Size 1 | Tiny Tots | Miniature ball, great for fun and skill development |
| Size 3 | Up to 8 years | Popular for youth leagues, easy to handle |
| Size 4 | 8 to 12 years | Ideal for transition, promoting skill refinement |
| Size 5 | 13 years and older | Standard for all adult leagues |
Modern balls commonly use butyl bladders for superior air retention and shape maintenance compared to latex alternatives. The journey of the soccer ball showcases a commitment to improving player performance while ensuring safety.

Future of Soccer: Trends and Developments
The future of soccer appears dynamic, shaped by several pivotal factors. Soccer trends indicate a notable shift towards technological integration, with artificial intelligence (AI) playing a crucial role. AI-powered software can analyze every move made by a player during a game, providing detailed insights that help coaches make real-time tactical decisions. This advancement in game developments allows for more informed strategies on the field.
In addition to tactical analysis, AI can predict player fatigue or injury risks by monitoring physical exertion and stress levels. This focus on player wellbeing represents a significant shift in how teams manage their athletes, enhancing overall performance. Furthermore, AI applications in scouting have transformed how clubs recruit players. By utilizing vast datasets, teams can predict player performance and fit more accurately, ensuring efficient recruitment processes.
The rise of technology extends to fan engagement. AI-driven chatbots now enhance how fans interact with clubs, while predictive models improve experiences in fantasy leagues. Such innovations aim to elevate the overall fan experience, making it more engaging and interactive. Companies like sKora Technologies exemplify the adoption of AI as they support aspiring footballers with tailored career opportunities.
Looking ahead, several trends are expected to shape the future of soccer:
- By 2030, Gen Alpha and Gen Z will represent 45% of the workforce, leading to significant shifts in sports industry trends.
- Technology, such as sensor-equipped soccer balls, will continue to enhance both player performance and fan engagement.
- Globalization is fostering new international cross-border leagues, reflecting changing fan preferences and the sport’s commercialization.
- Investment in players and technology is climbing, creating disparities between wealthy clubs and smaller teams.
- The growing prominence of women’s soccer is driven by increased support for gender equality, leading to rising participation rates and revenues.

The convergence of technology and soccer promises to revolutionize the sport, making it more equitable and exciting for everyone involved. As these factors continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly influence the direction of the game.
Conclusion
As we reflect on this comprehensive summary of the soccer guide, it is clear that soccer is more than just a sport; it is a global phenomenon that connects diverse communities worldwide. From its rich history to the current dynamics of play, appreciation for the beautiful game continues to flourish. The transition from smaller squads of 4v4 to more complex 11v11 formations illustrates not just logistical evolutions but a deeper understanding of defensive and attacking strategies that can foster a more enriching experience for players at every level.
The soccer community thrives on the passion of its players and fans alike, making it a driving force for cultural unity and personal development. Insights from coaches, like Wayne Harrison, emphasize the need to cultivate “thinking players” who can adapt on the field, while partnerships with organizations focused on soccer awareness, such as Amplified Soccer Marketing, enhance educational resources for aspiring athletes. This ongoing investment in education and self-improvement forms a solid foundation for the future of the game.
In contemplating the future of the game, it is paramount to recognize the role that unity through sport plays in both personal and communal growth. As soccer continues to be a vehicle for self-expression and dignity, the onus will remain on players and coaches alike to uphold the principles of excellence that this captivating sport demands. Embracing this journey not only honors the rich sporting tradition of soccer but also positions it as an ever-evolving odyssey for generations to come.

















Be the first to leave a comment